Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on preventing defects, while Quality Control (QC) involves identifying defects in the final product. Quality Assurance and Quality Control are fundamental concepts in the realm of manufacturing and service delivery, ensuring products meet or exceed customer expectations.
QA is a proactive process that aims to improve the development and production phases to prevent errors. On the other hand, QC is a reactive measure, inspecting and testing products to identify any faults before they reach the consumer. Both processes are crucial for maintaining high standards, yet they operate at different stages of the production cycle.
Quality Assurance and Quality Control
In Garment manufacturing, Quality assurance and control are the most crucial parts of Quality. With Quality products, we can satisfy buyers. Although quality assurance and quality control are closely related to garment manufacturing Quality, they are both aspects of Quality management. They are both committed to producing full, good-quality products per buyer requirements.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the differences between Quality Assurance and Quality Control and highlight their respective roles in ensuring excellence.
Defining Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance focuses on preventing defects. It ensures processes are in place to provide quality. QA is proactive. It involves planning, guidelines, and methodology development. The goal of QA is to improve development and test processes. This prevents any issues before they happen. Here’s what QA typically includes:
- Process Evaluation: QA checks if correct processes are in place.
- Standards Development: QA sets guidelines for project teams.
- Training: Teams receive proper process training.
- Documentation: QA requires detailed process recording.
Defining Quality Control
Quality Control is about finding defects. QC inspects the final product. It is reactive. QC steps in after products are developed. It tests products to find any defects. QC aims to identify and fix issues before the customer does. Quality Control involves:
- Inspection: QC examines products for flaws.
- Testing: It tests product parts and finished products.
- Problem Reporting: QC finds and reports issues.
- Feedback Loops: It uses feedback to improve products.
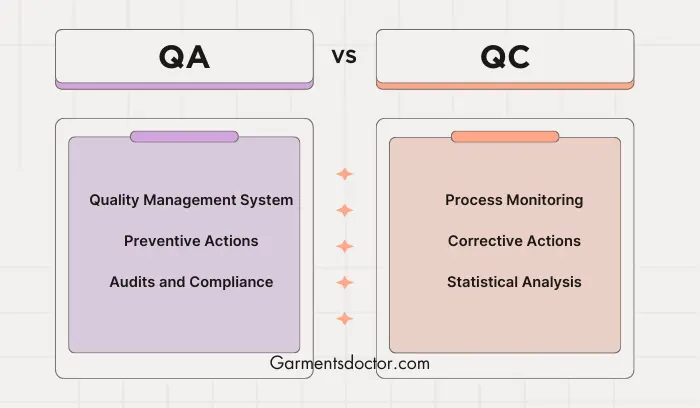
Difference Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
Although Quality Assurance and Quality Control are closely related concepts and both aspects of quality management, their focus is fundamentally different.
Quality Assurance
- QA systematic actions are necessary to ensure the product meets the required quality standards.
- It is process-oriented and focuses on defect prevention.
- QA aims to prevent defects when making a product. So, it is a proactive quality process.
- Prevention of quality problems through planned & systematic actions, including documentation.
- Everyone on the team developing a product is responsible for Quality Assurance.
- QA is the process of managing Quality.
- QA is considered a managerial tool.
Quality Control
- Quality Control ensures product quality in the first stage.
- It is product-oriented and focuses on defect identification & correction.
- QC aims to identify & correct defects in the finished product. So, it is a reactive quality process.
- The operational techniques and activities are used to achieve and maintain the Quality & process.
- A specific team involved in testing or identifying product defects is responsible for Quality Control.
- QC is used to verify the Quality of each process and output.
- QC is considered a corrective tool.
Roles And Responsibilities In Qa And Qc
Understanding the roles and responsibilities in QA (Quality Assurance) and QC (Quality Control) is crucial. These two areas ensure products meet standards. But, their tasks differ greatly. Let’s explore these differences in detail.
Qa Teams’ Duties
QA teams focus on preventing errors. Their main goal is to make sure processes are right. This leads to quality products. Here are their key responsibilities:
- Developing and maintaining quality standards.
- Ensuring all team members understand these standards.
- Conducting audits to check if standards are met.
- Identifying areas for improvement in processes.
- Training employees on quality management practices.
Qc Personnel Tasks
QC personnel focus on identifying defects in products. They work on already made products. Their goal is to find and fix errors. Here are their main tasks:
- Inspecting finished products to ensure they meet quality standards.
- Using tools and equipment to test products.
- Identifying defects and reporting them.
- Suggesting ways to fix defects.
- Recording test results for future reference.
Both QA and QC play vital roles in delivering quality products. QA ensures processes are right from the start. QC checks the final product for any mistakes. Together, they guarantee customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Both Quality Assurance and Quality Control ensure product Quality and service excellence. QC tries to find defects in root labels, and they provide a Defect-free product. At the same time, QA focuses on preventive action and tries to establish and maintain standard procedures like SOP. Ultimately, the combination of Quality Control and Quality Assurance depends on the organization’s needs.
Also Read: The Role Of Quality Control In Garments Industry (QC)
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the difference between QA and QC in the garment industry?
QA focuses on preventing defects in the manufacturing process, while QC involves detecting and correcting defects through inspection and testing.
Definition of Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance (QA) refers to a systematic set of actions, processes, and procedures that systematically monitor different aspects of a facility to detect correctness and ensure that required quality standards are being met.
Definition of Quality Control
Quality Control (QC) refers to the operational techniques and activities to fulfill product quality requirements. Quality Control is a process used to commit to the required Quality of a defect-free product.
Why are QA and QC important in the garment industry?
QA and QC ensure that garments meet quality standards, leading to customer satisfaction, brand reputation, and cost savings.



